Introduction
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Office of Health Equity launched a project under federal initiative OT21-2103 to reduce COVID-19 health disparities in vulnerable populations, including rural communities. As part of this effort, REDi Health was contracted to support independent rural hospitals in Utah that operate without integrated EMR systems.
In partnership with the Utah State Office of Rural Health (SORH), the project aims to standardize population health data collection, integrate population health into daily operations, and strengthen hospitals’ ability to analyze data related to social determinants of health, post-COVID syndrome, and chronic disease. It also supports building collaboration networks and community-clinical linkages to improve care coordination.
Key focus areas include:
Over an 18-month period, REDi Health partnered with six of nine independent rural hospitals in Utah. The original scope included identifying challenges and successes in implementing population health strategies, integrating them into daily operations, and improving data collection and analysis. REDi Health also supported efforts to build collaboration networks and community-clinical linkages.
As work progressed, it became clear that hospital engagement increased when the focus shifted to addressing immediate needs. The scope expanded to include solving problems related to scheduling, revenue integrity, manual processes, and data reporting. REDi Health’s goal is to help small and rural hospitals maximize their data and build long-term sustainability by strengthening financial health, clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, and population health, especially in relation to social drivers of health. This report captures key achievements, challenges, and insights from the participating hospitals.
The OT-21 initiative has driven major improvements in data collection, integration, and reporting across the participating rural hospitals. By automating manual processes, hospitals reduced staff burden, increased data accuracy, and streamlined decision-making—leading to more efficient operations and better clinical outcomes. These upgrades empowered hospitals to allocate resources more effectively and focus on high-value, preventive care.
Key successes include the implementation of comprehensive clinical registries and dashboards that support proactive patient management. Registries focused on diabetes, heart failure, depression, stroke, and other conditions helped providers shift from reactive to preventive care. By integrating data from EMRs, payers, and additional sources, hospitals strengthened their monitoring and reporting capabilities.
Hospitals improved revenue integrity and have seen financial gains through chargemaster reviews, denials automation, and DNFB reporting. These improvements streamlined billing, corrected reimbursement discrepancies, and strengthened financial stability. Additionally, tools like community care dashboards and wellness visit trackers helped close care gaps and support high-risk populations. Enhanced reporting around infections, antibiotic use, and COVID cases improved both care delivery and public health response—advancing health equity and population health outcomes across these rural communities.
The OT-21 initiative resulted in positive financial improvements for the hospitals. By increasing financial transparency, automating inefficient processes, and strengthening revenue integrity, the OT-21 initiative helped hospitals optimize operations and achieve immediate revenue growth.
Automation of processes resulted in significant time savings and improved accuracy. For example:
Efforts across five hospitals to improve denials management led to significant financial recoveries and faster billing processes. Tools like dashboards and quality reports reduced denials and improved payment timelines. Chargemaster reviews and payer reimbursement analyses uncovered underpayments and identified opportunities to optimize revenue.
To see a representation of financial reports, registries, and dashboards implemented across the six hospitals, reach out to sabrina.barnett@redihealth.com.
Specific successes in revenue integrity:
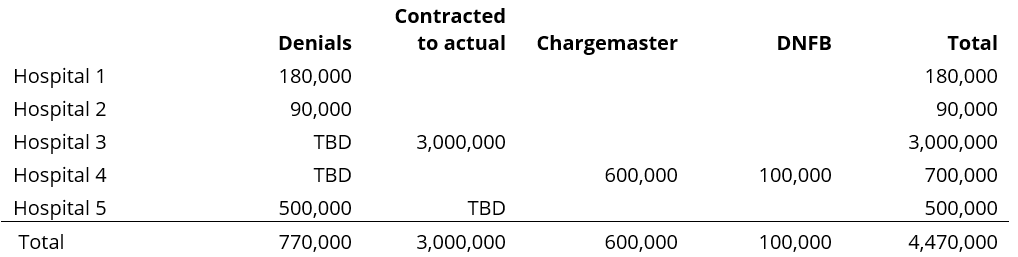
These efforts not only identify revenue opportunities but also support hospitals in recovering those funds. Some impacts are ongoing and not yet fully quantifiable. Below is a simple representation of the expected impacts on revenue in 2024.
The successes in the clinical area are closely tied to 4 main areas:
To see a representation the clinical registries, reports, and dashboards created for use across the six hospitals, reach out to sabrina.barnett@redihealth.com.
Specific successes at individual hospitals:
The initiative’s greatest achievements include the development of clinical registries and automated reporting systems that advanced preventive care, clinical outcomes, and operational efficiency. Key challenges include securing administrative support and managing system transitions which underscore the importance of data integration and automation in healthcare.
Operational successes focused on improving efficiency, eliminating manual work, and enhancing data-informed decision-making. The initiative also simplified regulatory reporting and supported more strategic, patient-centered care.
Key accomplishments include:
Some hospitals had unique needs that required tailored support during the project. REDi Health provided solutions such as:
To see a sample of the reports, registries, and dashboards created to ease operational burdens and help with future strategy, reach out to sabrina.barnett@redihealth.com. These dashboards have collectively improved care delivery, resource use, and system responsiveness.
The OT-21 project significantly improved public and population health capabilities across participating hospitals, strengthening readiness for future health emergencies and advancing disease prevention.
Population Health: Hospitals strengthened reporting around at-risk populations and preventive care, using data integration and targeted interventions to improve outcomes and public health preparedness in rural communities.
These key takeaways summarize the essential findings from the overall project across all 6 facilities, highlighting critical insights that underscore the transformative impact of data analytics in rural healthcare settings. After all, in the words of W. Edwards Deming, “Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.”
Several foundational elements are critical to ensuring reports, registries, and dashboards lead to meaningful improvements:
Note: While all these elements are vital to project success, leadership engagement sparks momentum, and change management ensures lasting impact. As Peter Drucker said, “The greatest wisdom not applied to action and behavior is meaningless data.”
The OT-21 initiative showcased the large impact of data analytics in rural healthcare and highlights significant advancements in financial management, clinical outcomes, operational efficiencies, and population health across 6 Utah hospitals. Despite challenges in staff availability and leadership transitions, these hospitals have laid a strong foundation for future growth and innovation in healthcare delivery. As they continue to integrate data-driven insights into their workflows, they are poised to achieve sustained improvements in patient care, operational performance, and community health outcomes and set a precedent for data-driven healthcare excellence in rural settings.

Fill out the form to connect with us, and let’s explore how we can support your hospital’s goals—one step at a time.